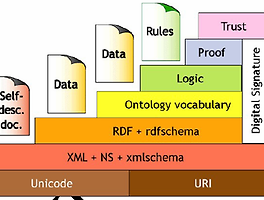
- Introduction
- RDF : Resource Description Framework
- W3C Recommendation
- Graphical formalism ( + XML syntax + Semantics)
- Triple에 기초한 간단한 Data Model을 제공함
[참고] Explicit Specificaiton 을 위한 다양한 언어들 (Graphic Notations)
- Semantic Networks
- Topic Maps
- UML
- RDF- Semantic Networks
- Object Oriented Models
- Objects/ Instances/ Individuals
- Types/ Classes/ Concepts
- Reations/ Properties/ Roles
- RDF Data Model
- Statements 는 Triples로 구성
<subject , predicate, object> e.g. <Sean, hasColleague, Ian>
- Statements 는 Triples로 구성
- Statement는 Resource의 속성을 묘사한다
- Resource란, URI을 통해서 지정될 Object이다.
- Linking Statement
- 한 Statment의 Subject가 다른, Object 가 될수 있슴
- RDF Syntax
- RDF 는 XML Syntax임
- 모든 "Description" element는 Resource을 묘사함
- "Descripton"내 모든 attribute와 인접한 element는 , Resource의 Property임
- URI로 resource을 참조함
<Description about="some.uri/person/sean_bechhofer">
<hasCollegue resource="some.uri/person/ian_horrocks"/>
<hasName rdf:datatype="&xsd;string"> Sean K. Bechhofer </hasName>
</Description>
- RDF(S): RDF Schema
- RDF 는 meta-data annotation에 대한 형식을 제공하는것이고,
XML 형태로 이를 기입하는 방법을 제공한다.
하지만, 'subClassOf' / 'type'과 같은 vocabulary에 대해 특별한 의미를 부여하지는 않는다 - RDF Schema는, RDF을 "Schema Vocabulary"로 확장한 것인데,
이는 기본 vocabulary term들과, 다음의 terms들간의 관계를 명시한다
- RDF 는 meta-data annotation에 대한 형식을 제공하는것이고,
extra meaning 인 semantic
- Class, type, subClassOf
- Property, subPropertyOf, range, domain
- RDF(S) Examples
<Person, type, Class>
<hasColleague, type, Property>
<Professor, subCalssOf, Person>
<Carole, type, Professor>
<hasColleague, range, Person>
<hasColleague, domain, Person>
- RDF/ RDF(S) "Liberality"
- Class와 Instance(Indivduals)간에 구별이 없다
<Species, type, Class> - Species->Instance , Class = Class
<Lion, type, Species>
<Leo, type, Lion>
- Property 역시, property을 가질 수 있다
<hasDaughter, subPropertyOf, hasChild>
<hasDaughter, type, familyProperty>
- Language constructor와 ontology vocabulary간에 구별이 없다.
따라서, 생성자는 자신한테는 다른 것한테든 적용 될 수 있다.<type, range, Class>
<Property, type, Class>
<type, subPropertyOf, subClassOf>
- Class와 Instance(Indivduals)간에 구별이 없다
- Restrictions & Notes
- Class 와 Property는 독립적으로 모델링 되어야 한다
- 일반적인 'Object-Oriented' modeling과 다른점이다.
일반적인 OO는 Properties가 Class의 일부분이기 때문이다. - 따라서, domain/ range statement는 매우 제한적으로 구성될 수 밖에 없다.
- 일반적인 'Object-Oriented' modeling과 다른점이다.
- 위 그림의 Level간 Line은 설명을 위한 것이다.
- RDF(S)는 매우 작은 범위의 "formal semantics"이다.
- RDF(S) statement 내 내포된 다른 Statement가 무엇인지 명시해야 함
- 다른 구성들간에 몇몇 Content에 대한 상호 협정이 필요하다.
(RDF(s)와 다른 언어간의..) - RDF 문제점들..
- RDF는, resource을 자세히 기술하기에는 매우 약하다
- No localised range and domain constraints
'hasChild' 의 range가 'Person' 에 있는지, 'Elephant'에 있는지 알수가 없다 - No existence/ cardinality constraints
'Person'의 모든 instance가 'mother'을 갖는지 알수가 없고,
'Persons'는 정확히 2명의 부모를 갖는다고 알수가 없다. - No transitive, inverse or symmetrical properties
- Reasoning 지원을 제공하기는 어렵다
- No native reasoners for non-standard semantics
- 해결책
- RDF(S)는 다음의 특징들을 따르는 language (OWL)로 확장한다.
- XML, RDF, RDFS와 같은 Web 표준으로 확장
- 이해하기 쉽고, 사용하기 쉽게
- automated reasoning 지원